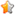Definition of Homolog, Ortholog and Paralog
It was suggested that I might want to provide definitions which made the difference between these terms clear. These definitions are provided here.
Homolog- A gene related to a second gene by descent from a common ancestral DNA sequence. The term, homolog, may apply to the relationship between genes separated by the event of speciation (see ortholog) or to the relationship betwen genes separated by the event of genetic duplication (see paralog).
- Orthologs are genes in different species that evolved from a common ancestral gene by speciation. Normally, orthologs retain the same function in the course of evolution. Identification of orthologs is critical for reliable prediction of gene function in newly sequenced genomes. (See also Paralogs.).
- Speciation is the origin of a new species capable of making a living in a new way from the species from which it arose. As part of this process it has also aquired some barreir to genetic exchage with the parent species.
- Paralogs are genes related by duplication within a genome. Orthologs retain the same function in the course of evolution, whereas paralogs evolve new functions, even if these are related to the original one.
See the following NCBI diagram Orthology which shows the relationship between the three terms.